Introduction about Sarcoma Cancers:
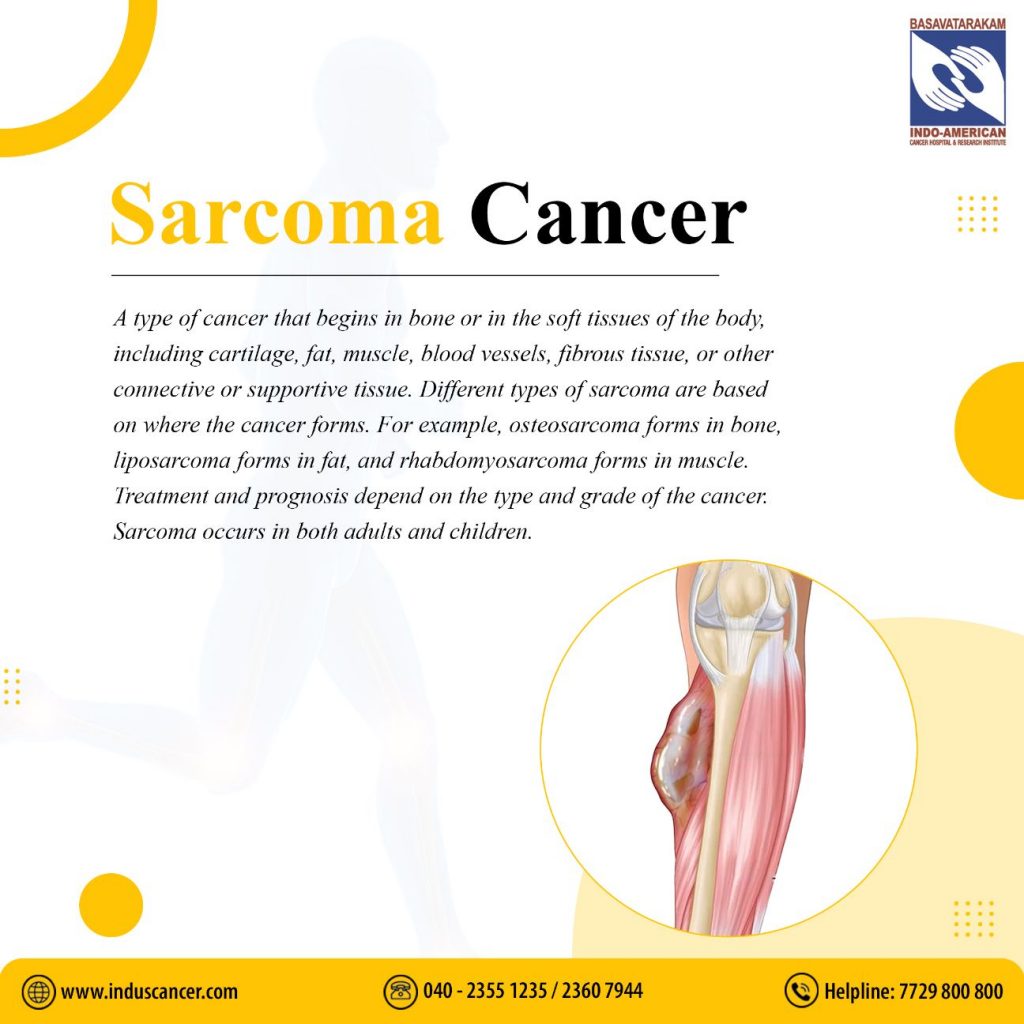
As we continue our mission to raise awareness about various cancers, we turn our focus to sarcoma cancers. This detailed guide aims to provide comprehensive information about sarcomas, shedding light on their types, causes, signs, diagnosis, and treatment options. At Basavatarakam Indo American Cancer Hospital, we believe in empowering our patients, their families, and the community at large with knowledge to better understand and manage this rare group of cancers. Sarcoma is a type of cancer that develops in the body’s connective tissues, which are the tissues that support and connect various structures in the body. These tissues include bones, muscles, tendons, fat, blood vessels, nerves, and other soft tissues. Sarcoma can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the arms, legs, chest, abdomen, and retroperitoneum (the area behind the abdominal cavity). Although they account for a small percentage of all cancer cases, understanding sarcomas is essential due to their unique characteristics and treatment requirements.
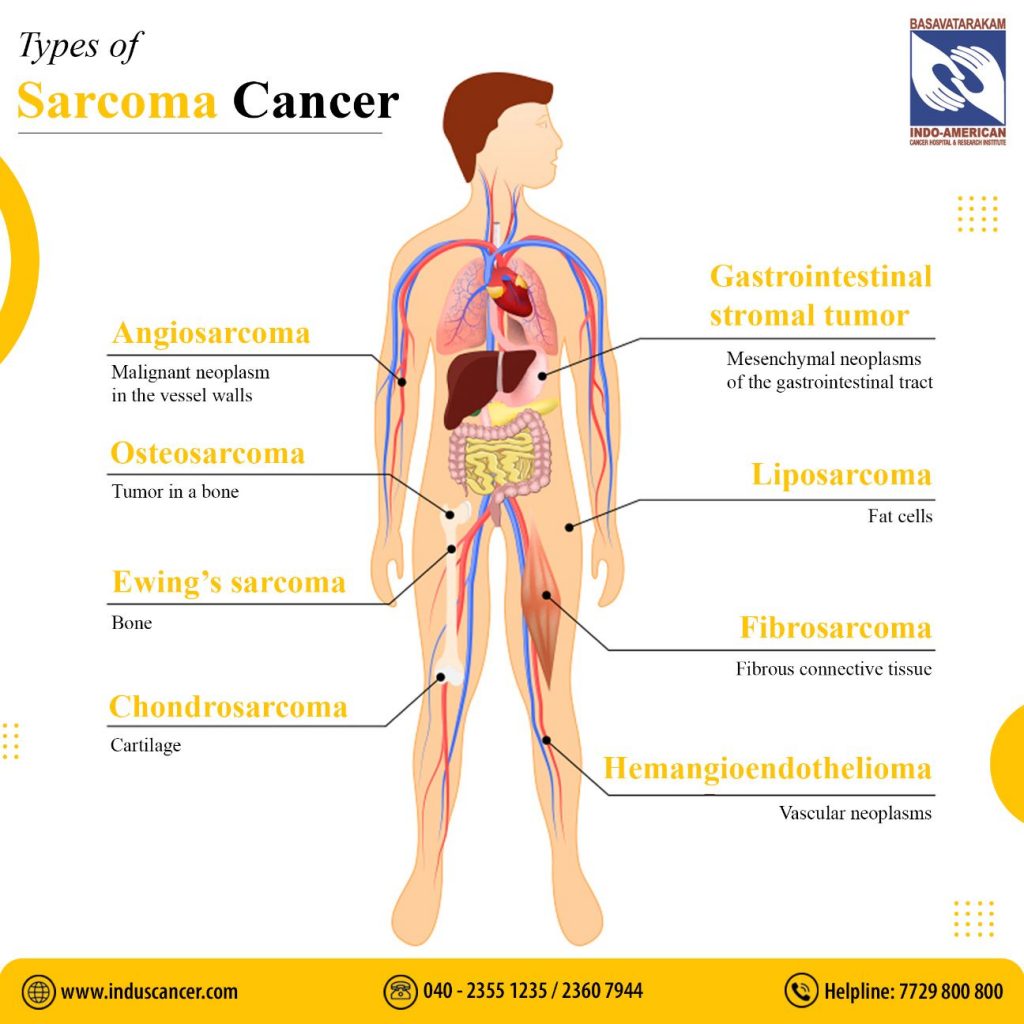
Types of Sarcoma Cancers:
Soft Tissue Sarcomas: These tumors originate in the body’s soft tissues, including muscles, fat, tendons, nerves, blood vessels, and other connective tissues. They can develop anywhere, but they are most commonly found in the arms, legs, abdomen, and retroperitoneum.
Bone Sarcomas: Bone sarcomas, as the name suggests, arise in the bones. They can affect individuals of all ages and include subtypes such as osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, and chondrosarcoma.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of sarcoma cancers remains elusive, but certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing these tumors:
Genetic Predisposition: Family history of sarcoma or genetic syndromes like Li-Fraumeni syndrome and neurofibromatosis.
Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation therapy for other cancers can elevate the risk of sarcoma development.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins may play a role in sarcoma formation.
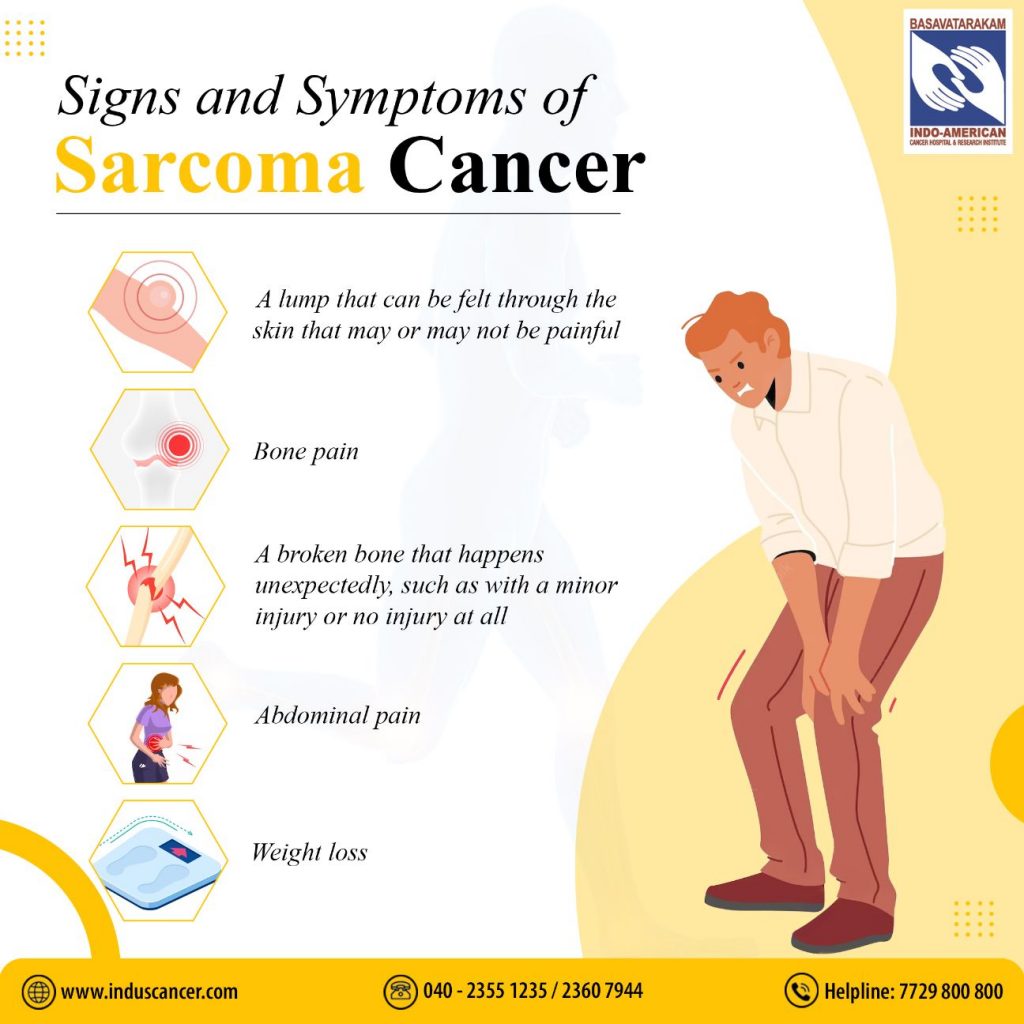
Signs and Symptoms:
Early detection is vital for better outcomes. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of sarcoma can lead to timely medical attention. Common indicators include:
Lumps or Swellings: Unusual growths or masses in soft tissues or bones.
Persistent Pain: Continuous pain or discomfort in the affected area.
Limited Mobility: Difficulty moving a limb or experiencing joint stiffness.
Fatigue and Weight Loss: Feeling excessively tired or experiencing unintended weight loss.
Bone Pain: Persistent pain in bones, especially during activity or at night.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
Diagnosing sarcoma cancers requires a thorough evaluation by a multidisciplinary team of experts. The process typically involves:
Physical Examination: The healthcare provider assesses the lump or affected area and inquires about symptoms and medical history.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and PET scans help visualize the tumor’s location, size, and extent of spread.
Biopsy: A tissue sample is obtained to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the specific sarcoma type.
Pathology and Molecular Testing: Sophisticated laboratory analyses identify genetic mutations that may influence treatment decisions.
Treatment Approaches:
The treatment plan for sarcoma cancers depends on various factors, including the tumor type, stage, and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment modalities include:
Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the primary treatment for localized sarcomas. Limb-sparing surgery is prioritized whenever feasible.
Radiation Therapy: Some sarcoma respond to radiotherapy. High-energy X-rays target and destroy cancer cells. It can be used before surgery (neoadjuvant), after surgery (adjuvant), or as palliative treatment.
Chemotherapy: Some sarcoma types respond to chemotherapy, either alone or in combination with other treatments.
Targeted Therapies: Emerging treatments target specific genetic mutations in sarcoma cells, disrupting their growth and division.
Immunotherapy: Clinical trials explore the use of immunotherapy to enhance the body’s immune response against sarcoma cells.
Conclusion:
Sarcoma cancers are a challenging group of tumors that demand specialized care and expertise. At Basavatarakam Indo American Cancer Hospital and Research Institute, our dedicated team is committed to providing comprehensive and compassionate care for sarcoma patients. By spreading awareness and understanding, we aim to promote early detection, timely intervention, and improved outcomes. If you or someone you know is concerned about sarcoma, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice from our experienced professionals.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical advice. For specific healthcare recommendations, consult our qualified medical professionals at Basavatarakam Indo American Cancer Hospital and Research Institute.
Contactus at Toll Free Numbers: 040 – 2355 1235 / 7729 800 800